Lesson 1.
Heroic introduction in
And also:
- History of HTML and its significance
- Key concepts
- Editing HTML
- Publishing our first HTML page on the internet
- Learning the first HTML tags
Part 0.
Preparing for the Lesson
Software
We will need two programs for our work:
- Visual Studio Code © - we will write code here.
- Google Chrome © - we will view the results here.
Both programs support plugins from third-party developers.
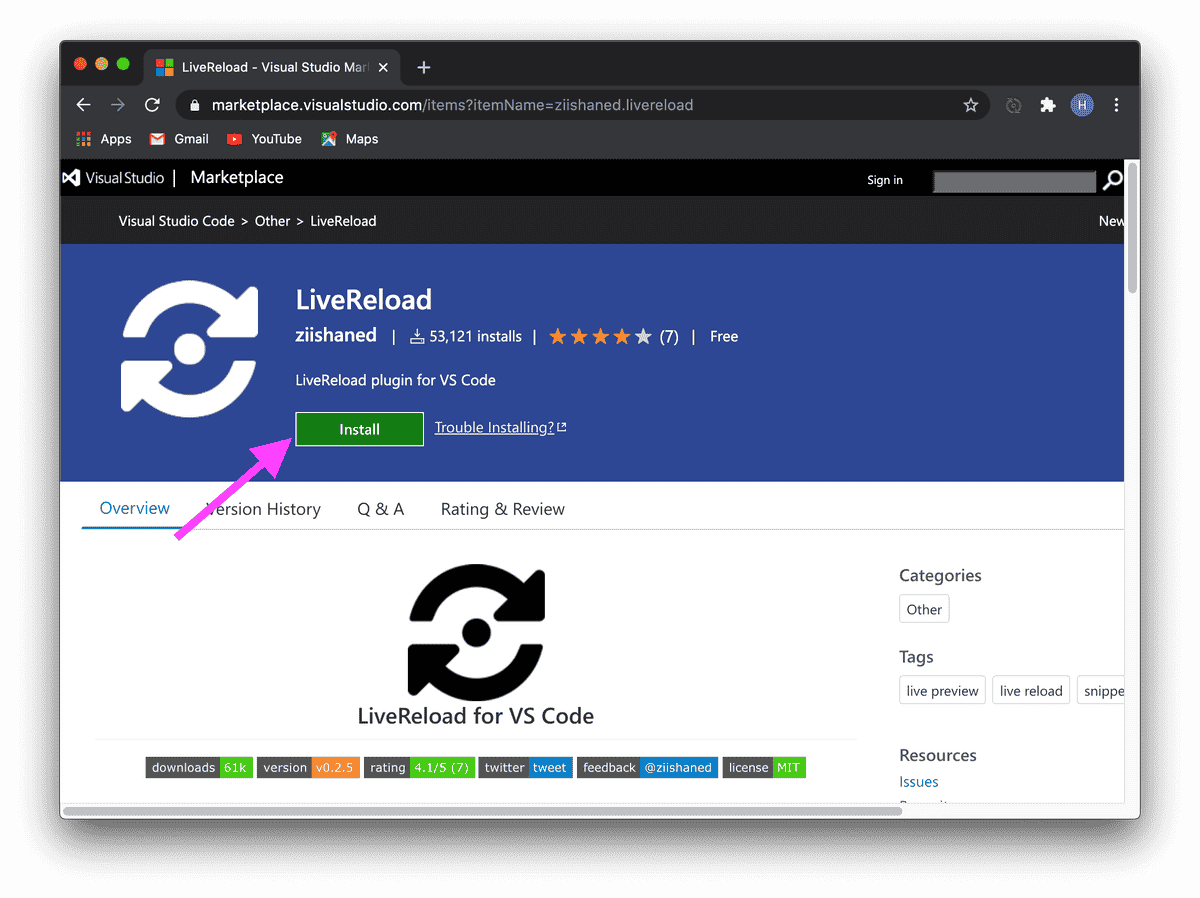
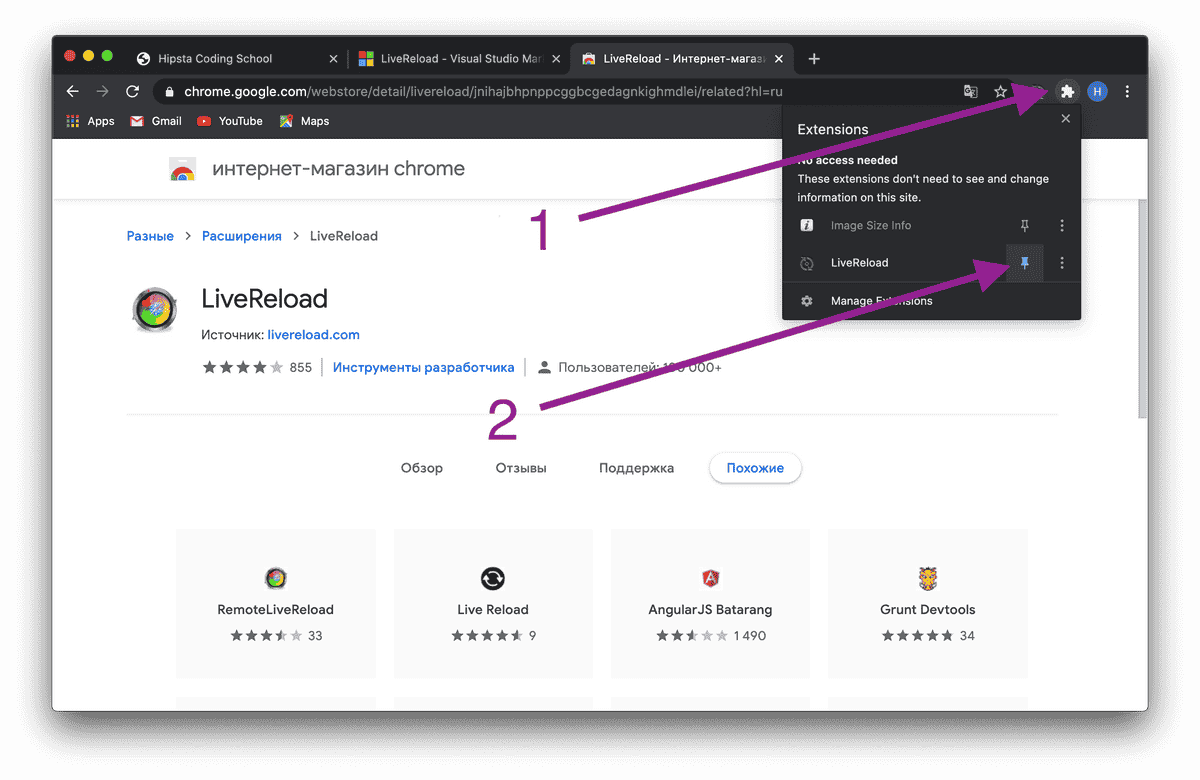
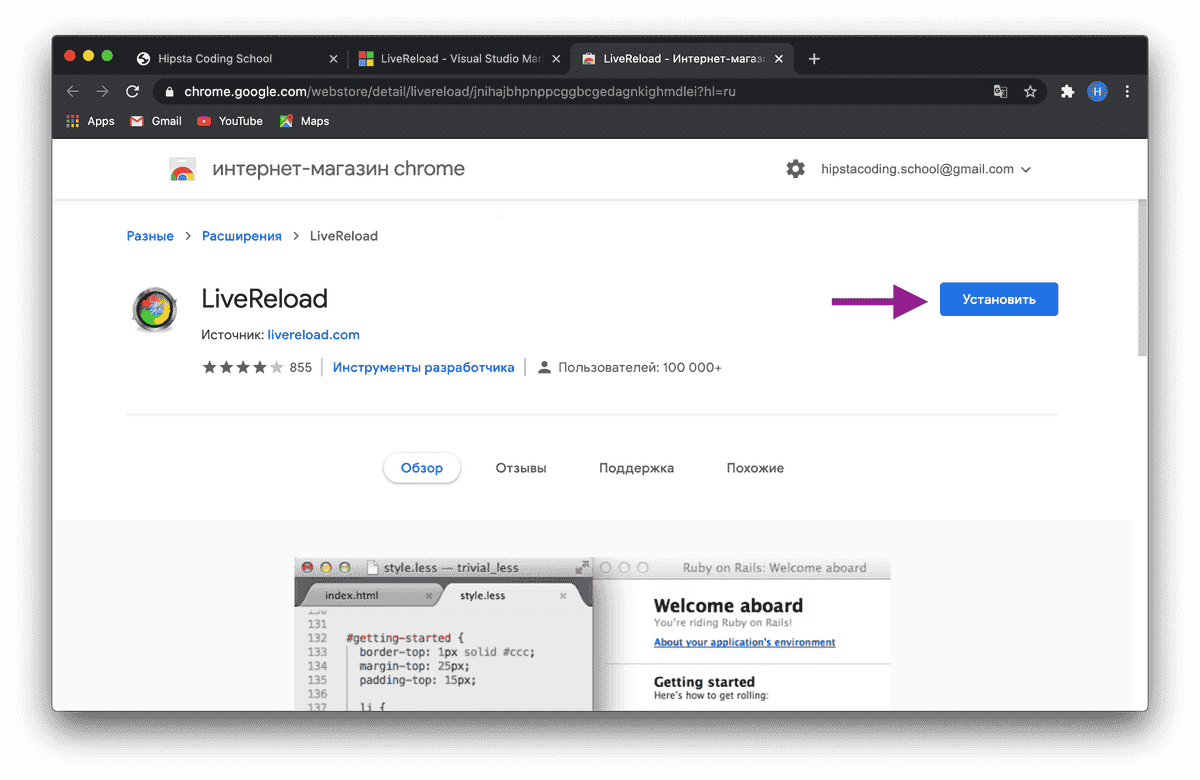
To avoid manually refreshing the page, we will use the LiveReload © plugin for Visual Studio Code © and Google Chrome ©.
To get started, simply install them.
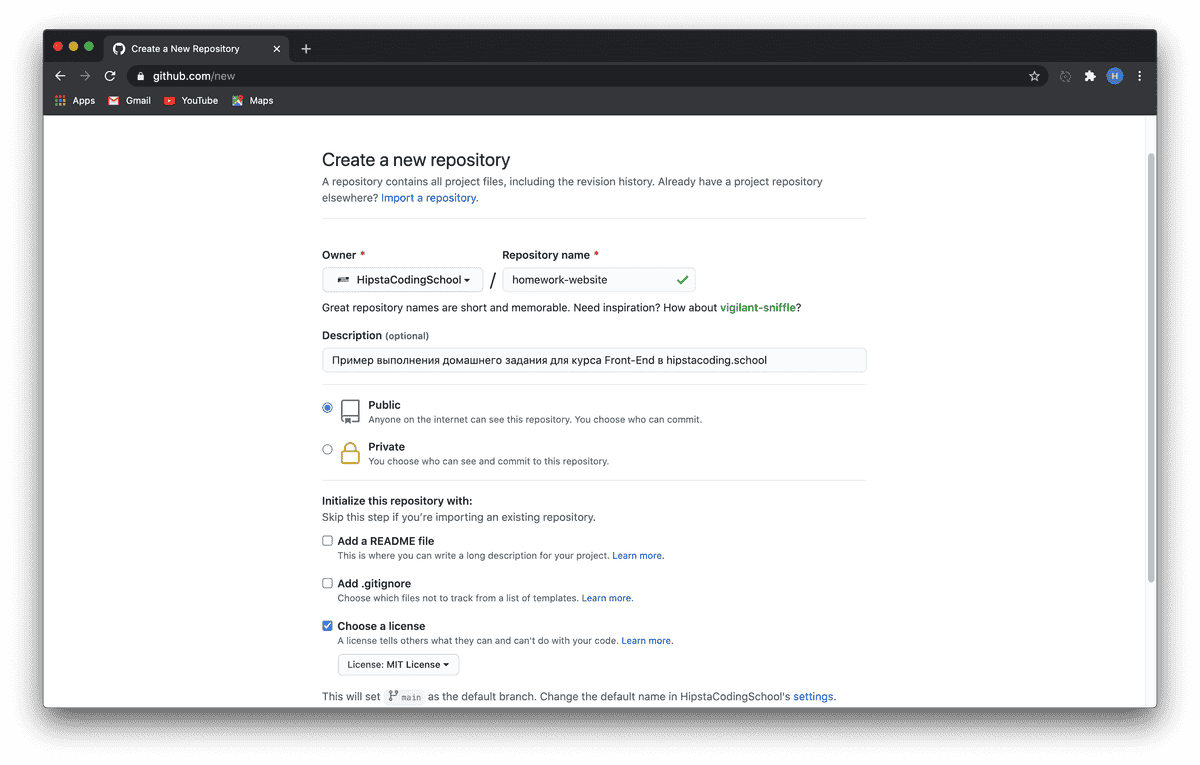
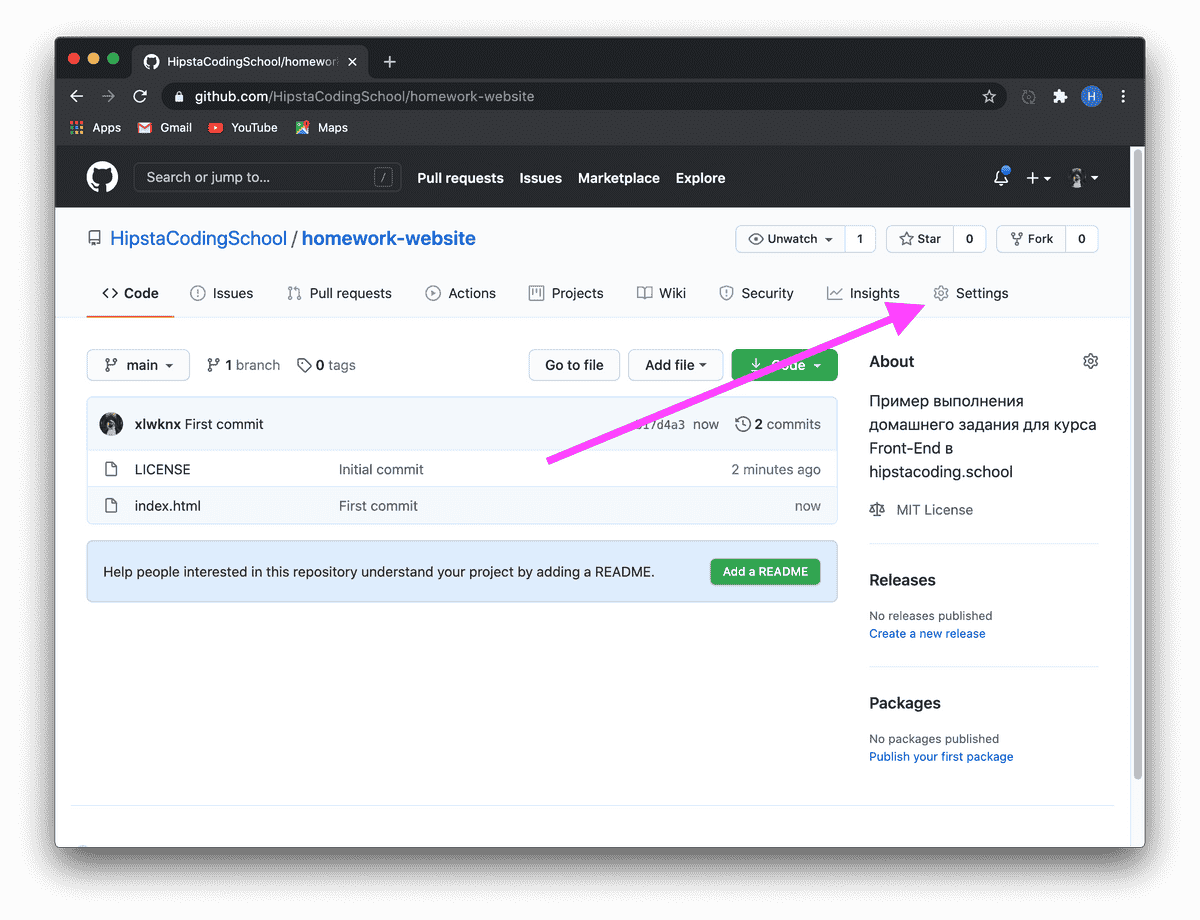
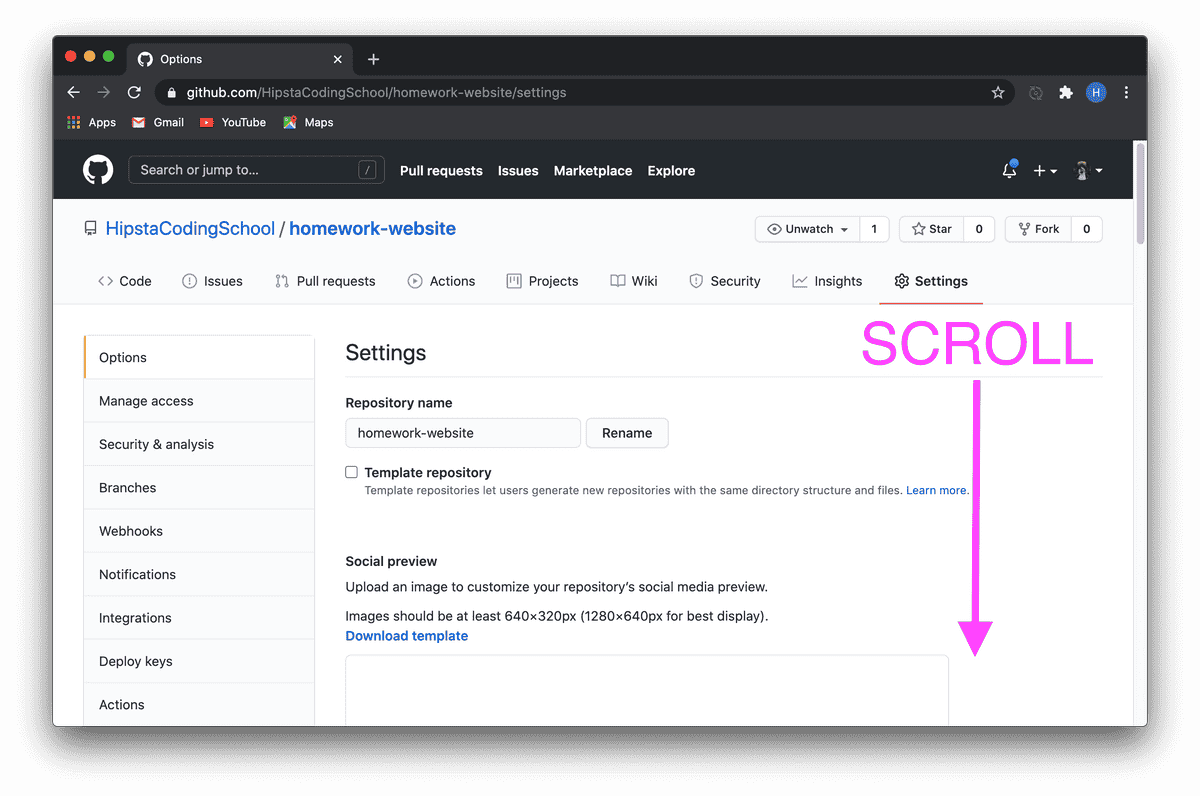
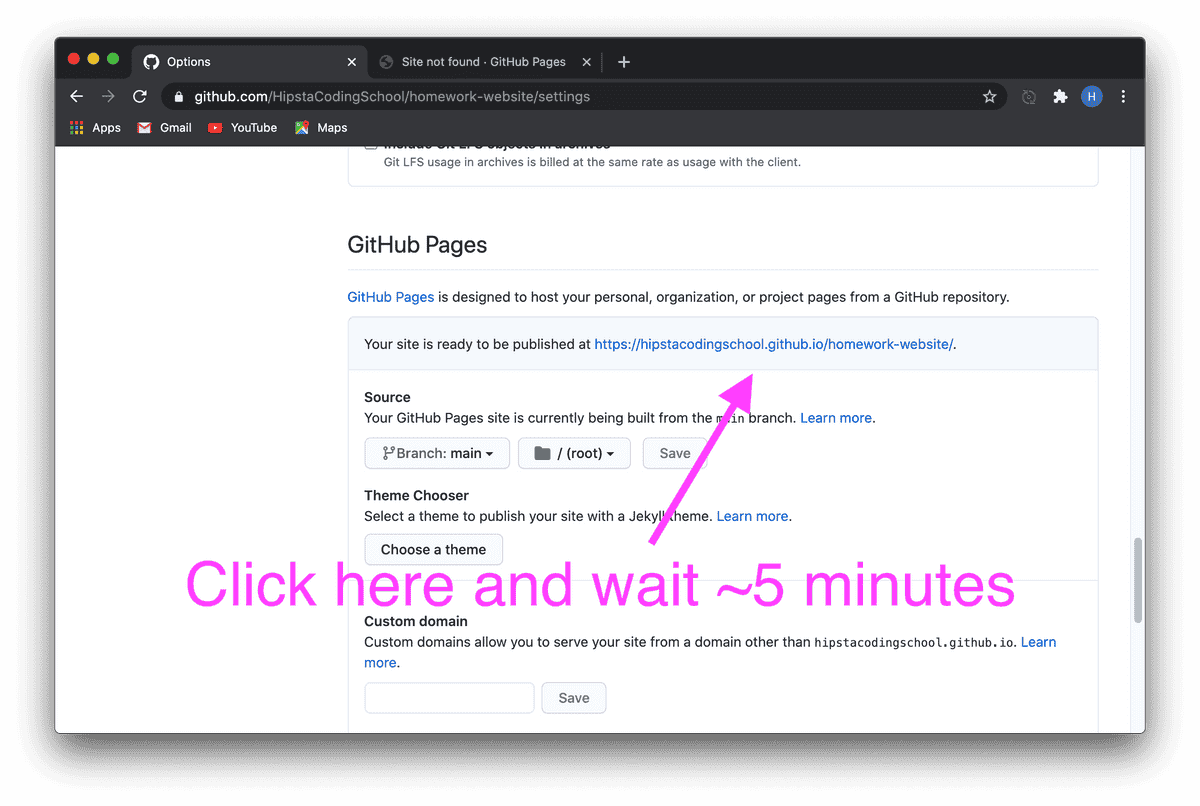
GitHub
I call it a social network for programmers, where instead of photos and posts, your code is showcased. To get started, simply register and, if you wish, add me as a friend and give a like (star) to the hipstacoding website.
Part 1.
History of HTML
1991
- The same guy invents the HyperText Markup Language, also known as HTML, designed for structuring and formatting documents on the World Wide Web.
- This year marks the appearance of the world's first website
First Browser War
1995-1999
Netscape vs Internet Explorer
Second Browser War or "Browser Zoo"
2005-2015
Internet Explorer vs:
- Netscape, which became Mozilla Firefox
- Apple Safari
- Opera Mini
- Google Chrome
Why is HTML needed and who needs it?
Front-End Developers
Front-End developers need to have a thorough understanding of HTML and CSS. The Front-End development process looks like this:
- Building the document structure using HTML.
- Adding styling using CSS.
- Writing JavaScript code for interactive components.
All Other Developers
HTML is still the best and sometimes the only way to create a user interface.
UI/UX Designers
Any good UI/UX designer should know how HTML and CSS work in order to create proper interfaces. Additionally, a designer who can code will be more valued in the job market.
SEO Specialists
For client-side search engine optimization, it is necessary to modify HTML tags, albeit sometimes indirectly.
Marketers
Marketers usually do not know HTML, but they deal with emails written in HTML on a daily basis, as well as services that are embedded into websites through HTML (e.g., Google Analytics). Therefore, they constantly rely on developers to assist them. By having knowledge of how HTML works, they can do it themselves and thereby increase their market value.
Key concepts
Browser
- a program through which you access the Internet.
Good newsBad news
HTML
- a standardized markup language for web pages on the World Wide Web.
© Wikipedia
HyperText
- text that differs from ordinary text in that it contains hyperlinks (here
Markup language
<b>Markup Language</b> <i>(from English: Markup Language)</i>
- a way of writing text that contains additional
information about its presentation or structure.
Getting Started with HTML
If we simplify it greatly, the internet is a collection of HTML files that are hosted on special computers called servers.
Let's create your first HTML file!
| Action | 🔥 Hotkey / Icon |
|---|---|
| Create a folder my-website | ⌘⇧N |
| Open VSCode | |
| Open folder in VSCode | ⌘O |
| Create a new file | ⌘N |
| Save the empty file | ⌘S |
| Name the file index.html | ⏎ |
| A little bit of magic | !↹ |
In WEB the first page that is opened to the user to be named index.html.
To facilitate development, it is recommended to install the LiveReload plugin, which will automatically reload the page every time we save it.
:⌘⇧P -> LiveReload: Enable/Disable server: Click on the Structure of page in HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta
name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Name of the tab</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Visual part goes here -->
</body>
</html><!DOCTYPE html>The <!DOCTYPE html> declaration tells the interpreter that HTML version 5 will be used in the document.
<html lang="en">
</html>The <html> tag is the opening tag for an HTML document. It is a required root tag. The lang attribute specifies the language of the document and is also required.
The lang attribute accepts values in the BCP47 format. It may sound intimidating, but in practice, it is mostly "en" for English. However, if you need to specify another language, you can find or verify its code using the provided link.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta
name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Name of the tab</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Visual part goes here -->
</body>
</html><head>
</head>The head tag contains meta-information for the browser. Here is a list of tags that it can include.
<meta />
The meta tag describes metadata.
Metadata is data that describes other data. Meta tags heavily depend on the attributes declared within them.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta
name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Name of the tab</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Visual part goes here -->
</body>
</html> <meta charset="UTF-8">The meta tag specifies the character encoding.
Gibberish characters in 99.9% of cases indicate encoding issues.
If gibberish characters appear in the browser, it means the charset attribute in the meta tag was incorrectly specified.
If gibberish characters appear in a file, it means either the file was saved with the wrong encoding or it is being read with the wrong encoding.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta
name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Name of the tab</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Visual part goes here -->
</body>
</html> <meta
name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">The meta tag responsible for proper display on mobile phones. In essence, it specifies that the viewport width should be equal to the device width, and the initial scale should not be changed (neither zoomed out nor zoomed in, but set to 1).
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta
name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Name of the tab</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Visual part goes here -->
</body>
</html> <title>Name of the tab</title>The title of the tab. It is very important for search engine optimization.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta
name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Name of the tab</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Visual part goes here -->
</body>
</html><body>
<!-- Visual part goes here -->
</body>The body tag of the document. It contains the visual content of the HTML document. There can only be one <body /> tag on a page.
Text in HTML
HTML
don't care
about
indentation,
tabulations,
or more than one space
▲
▲ ▲
| description | symbol | letter code | numeric code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-breaking space | |   | |
| Space | none 😔 |   | |
| Ampersand | & | & | & |
| Less than (less then) | < | < | < |
| Greater than (greater then) | > | > | > |
Full list of HTML special characters
Indentations are achieved using the <p /> tag, which is named after the word "paragraph".
The HTML specification prohibits nesting <p /> tags inside another <p /> tag, so indentations within <p /> are achieved using the <br /> tag.
Headings in HTML
<h1>Heading level 1</h1>
<h2>Heading level 2</h2>
<h3>Heading level 3</h3>
<h4>Heading level 4</h4>
<h5>Heading level 5</h5>
<h6>Heading level 6</h6>
HTML Property No. 0
HTML allows you to make mistakes
For example, nothing prevents you from having multiple h1 headings on a page, but it is considered that there should be only one.
Indentation in HTML
<p>
Indentation in HTML is achieved using the <p> tag.
</p>
<p>
Indentation within the <p> tag is created using the <br /> tag.
</p>
HTML Property №1
Tag Pairing
- Paired tags can contain text within them (such as the
<p></p>tag). - Non-paired tags cannot contain text within them (such as the
<br />tag).
Lists in HTML
<ul>
<li>Unordered list item 1</li>
<li>Unordered list item 2</li>
</ul>
- Unordered list item 1
- Unordered list item 2
<ol>
<li>Numbered list item 1</li>
<li>Numbered list item 2</li>
</ol>
- Numbered list item 1
- Numbered list item 2
HTML Property No. 2
Tag Nesting
Nesting - the property of tags to contain other tags.
The most important rule of nesting is that the last opened tag should be closed first.
<ul><li>Element of the list</ul></li> <!-- Incorrect -->
<ul><li>Element of the list</li></ul> <!-- Correct -->
Links
<a
href="https://hipstacoding.github.io/"
target="_blank"
title="Click me"
>
Link text
</a>
HTML Property No. 3
Tag Attributes
An attribute (tag attribute) is an additional property of HTML elements. All HTML elements have common attributes and specific attributes.
All attributes in HTML are treated as strings.
The attribute href (Hyper REFerence) accepts the URL address of a link.